A common question asked is what do all the figures on my line stats mean? On this page and the next I will attempt to explain some of the data output by your router.
Line stats can be a useful aid in helping to identify faults and problems on your line, but before we start its important that we look at the whole picture and be aware that router line stats can be "snap shot" at any one particular moment in time and some figures are likely to change (particularly Noise Margin) over the course of the day.
Also note that different routers may report different figures on the same line therefore these figures should only be taken as a guide.
|
|
|
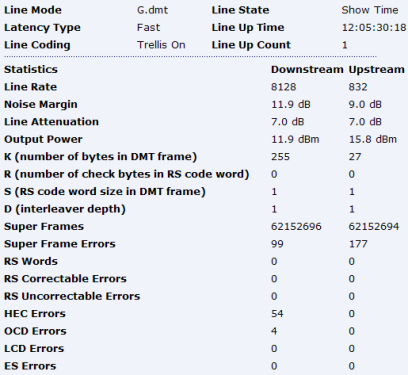
Line Stats from Voyager router
|
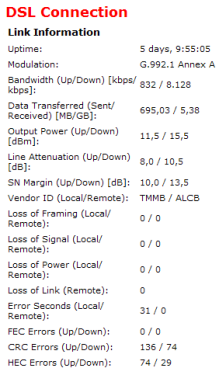
Linestats from Speedtouch router
|
~ Line Rate, Connection Speed, Bandwidth, Synchronisation Speed.
The speed at which your router has synchronised to the DSLAM at the exchange at. This is commonly called your sync speed.
It should not be confused with your actual throughput (real time) speed since it has an allowance to cover IP, ATM and other various overheads. The maximum throughput speed on a line syncing at 8128 under ideal conditions would be just slightly over 7Mbps. Other factors such as exchange contention, ISP restrictions or your IP profile will affect your actual throughput speed.
~ SNR Margin, Noise Margin, SN Margin, Local SNR Margin.
The downstream (or local) SNR Margin is normally the most important figure, as this can have an effect on your achievable downstream speed. SNRM can continually fluctuate depending on various conditions. The higher the SNR figure the better. Because SNR plays such an important role on your adsl connection there's a more in depth explanation on my interpreting your line stats page.
~ Line attenuation, Loop Loss, atten.
Attenuation is the degradation of signal over distance and an indication of the length of your line.
The lower this figure the better. Generally speaking there isn't much you can do about attenuation, because of its direct correlation to your distance from the exchange. Because attenuation is an important aspect of your line and the part it plays in adsl there is a more in depth explanation on the
interpreting your line stats page.
~ Output power
The amount of power transmitted from the exchange and your modem.
Output power will likely increase depending on the length of your line (loop loss).
|
|
In this context dBm represents the power ratio of decibels relative to milliwatts, and each 3dB increase is an approx doubling of the power output.
The tool on the right converts dBm into milliwatts. |
|
With adsl2+ most lines will be running to their maximum capability, and a figure of around 18-19 dBm is the norm. |
~ Attainable Rate, Max Rate
The sync rate you could attain if any line card or DSLAM restrictions were removed.
If you see a figure like then this is likely the restriction of the DSLAM on ADSL1. With adsl2+ its possible to get higher speeds. - See also RCO.
~ RCO - Relative Capacity Occupation
The existing sync rate expressed as a percentage against the Maximum Attainable Rate.
For example if you were sync'd at 8128 kbps because of restriction at the dslam or on your account, but the router estimates that your line is capable of 16Mbps, then the RCO would be 50% as you would only be using 50% capacity.
Something to be aware of though, is if your line is not running at full power because say of adsl1 restrictions, then it may not be able to reflect the RCO for adsl2+ accurately.
~ Line Uptime
Most routers will show various up times, each of which are different.
Line uptime is usually the time your router has remained connected to the DSLAM.
Broadband or Internet Connection is usually the time you have remained connected to your ISP (PPP session). Some routers will also show how long the router has been powered up for.
~ Channel Mode or Latency Type
Either FAST or INTERLEAVED. Fast is normal mode, Interleaving can be applied to the line to help increase stability.
~ Modulation, Line Mode
Type of ADSL Modulation used. eg
g.dmt = ADSL1. G.992.5 Annex A = ADSL2+. G.992.5 Annex M = ADSL2+ with increased upstream.
| |
ADSL1 |
ADSL2 |
ADSL2+ |
VDSL |
VDSL2 |
| Standard |
G.992.1
(G.DMT) |
G.992.3 |
G.992.5 |
G.993.1 |
G.993.2 |
| Max Downstream |
8 Mbps |
12 Mbps |
24 Mbps |
40 Mbps |
80 Mbps |
| Annex A |
Annex B |
Annex I |
Annex L |
Annex M |
DSL over POTS
(telephone) |
DSL over ISDN digital services |
Utilises voice frequency ranges for additional 256kbps upstream |
Extended Reach - increases range of DSL service up to 7KM |
Upstream frequency range increased to 276kHz for > 3.5Mbps |
VDSL2 Profile8c
Bandplan EU128 |
VDSL2 Profile17a
Bandplan 998-M1x-A |
|
|
|
~ Vendor ID
Identifies the type of chipset used in ADSL modems & DSLAM/MSANs.
Local is your router. Remote is the DSLAM.
| ID |
Manufacturer |
ATUC Code |
* DSLAM |
ALCB
BCLA |
Alcatel |
414C4342 |
STMicro
Alcatel |
| ANDV |
Analog Devices (ADI) |
414E4456 |
Cisco
Hyundai
Nortel |
| BDCM |
Broadcom |
4244434D |
Ericsson
Huawei (FTTC) |
| CNXT |
Conexant |
|
|
GSPN
NSPG
GPN
GPSN |
Globespan |
4753504E |
NEC
(Easynet) |
| IKNS |
Ikanos (previously Conexant) |
494B4E53 |
|
| IFTN |
Infineon (now Lantiq) |
4946544E |
Huawei MSAN
ECI (FTTC) |
| META |
Metanoia |
|
|
| STMI |
STMicro |
53544D49 |
Alcatel |
| TCTN |
Trend Chip Technologies Corp |
5443544E |
|
| TMMB |
Thomson MultiMedia Broadband
(TMMB is their brand Broadcom chipset) |
544D4D42 |
|
| TSTC |
Texas Instruments (TI) |
54535443 |
Marconi
Ericson
Huawei |
| µ |
Micro Electronics (STMicro) |
|
|
*There have been discussions about the interoperability between router and DSLAM chipsets. This column is a list of DSLAM manufacturers reported to have used certain chipsets. This list is only as a guide, if you have further info on DSLAM's chipsets please let me know.
~ Line State
This shows the state of the connection (sync) between the modem and DSLAM
at the exchange.
Not all routers will
show every step, but the most important stages are:
- Down (no sync)
- Handshaking (initial "hello" between modem and
DSLAM)
- Training
(establishing sync)
- Show Time (successfully synced)
The line state must be "Show Time" before a connection to your ISP can
be established.
See next page for linestat parameters and counters
|



